Crop conditions trended slightly below average throughout the monitoring period according to the crop condition development graph based on NDVI. The sowing of winter wheat was completed in October. The temperature was above average (TEMP +0.4℃), radiation was average and rainfall was below average (RAIN -19%) as compared to the 15YA. The lack of rainfall resulted in a slight decrease in the BIOMSS index by 9% as compared to the 15YA. The Cropped Arable Land Fraction (CALF) decreased by 5% compared to the recent five-year average and the national average of maximum VCI index was 0.53. The national Crop Production Index (CPI) was 0.89, indicating a relatively lower-than-normal crop production condition.
According to the spatial distribution of NDVI profiles, approximately 12.6% of the cropland (marked in blue) had above-average crop conditions during the whole monitoring period. The crop conditions of 41.1% of the croplands, marked in red, were near average. 11.3% of the cropland (marked in orange) had below-average crop conditions, mainly distributed in the northern parts of East Azarbaijan and Ardebil, and the province of Mazadaran. Crop conditions in the rest of the cultivated areas (marked in light and dark green) all had near-average to above-average crop conditions at first and then dropped to below-average at the end of the monitoring period, mainly in the provinces of Zanjan, Kordestan, Gilan, Hamadan, Kermanshah, Qazvin, Ilam, Lorestan, and Markazi. The spatial pattern of maximum Vegetation Condition Index (VCIx) was in accord with the spatial distribution of the NDVI profiles. The drop in NDVI in January can be attributed to cloud or snow cover. Overall, the crop conditions for winter crops were slightly below average.
Regional analysis
Based on cropping systems, climatic zones and topographic conditions, three sub-national agro-ecological regions can be distinguished for Iran, among which two are relevant for crop cultivation. The two regions are referred to as the Semi-arid to sub-tropical hills of the west and north, and the Arid Red Sea coastal low hills and plains.
In the Semi-arid to sub-tropical hills of the west and north region, crop conditions were slightly below average during the whole monitoring period. This AEZ is a mountainous, relatively high-altitude region. Snow cover is common, and thus the low NDVI values observed for January are not representative. Temperature was 0.6°C above average, the accumulated rainfall was 159 mm (21% below average), and radiation was slightly above average (RADPAR +1%). The unfavorable weather conditions resulted in a decrease of BIOMSS by 13% compared to the recent 15-year average. The CALF decreased by 11%, and the average VCIx (0.54) was rather low. Crop conditions were slightly unfavorable.
The Arid Red Sea coastal low hills and plains region had below average crop conditions during the whole monitoring period except for late January. This AEZ received 169 mm rainfall during the reporting period, 12% below the 15YA average (RAIN -12%). Temperature was 1.5°C above average (TEMP +1.5℃), and radiation was 3% below average (RADPAR -3%). BIOMSS was above average (+13%) as a result of relatively agreeable hydrothermal conditions. The CALF increased by 22% compared to the 5YA, reflecting that more land was cultivated. The average VCIx of this region was 0.64. Crop conditions were assessed as fair.
Figure 3.21 Iran's crop condition, October 2022 - January 2023
(a) Phenology of major crops
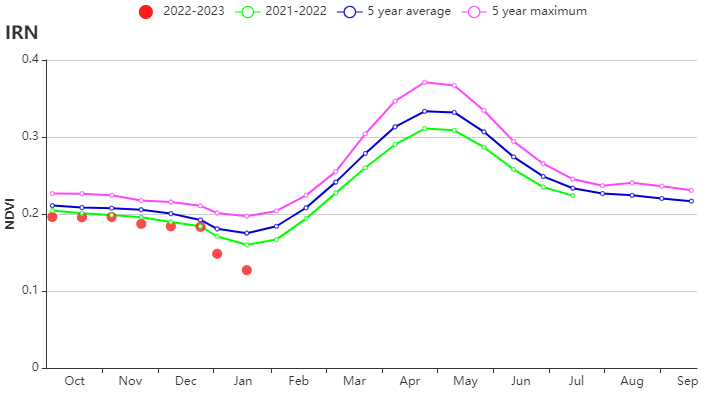
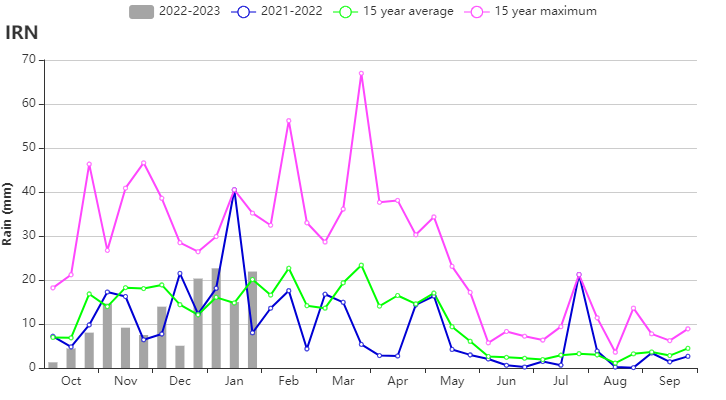
(b) Crop condition development graph based on NDVI (c) Time series rainfall profile
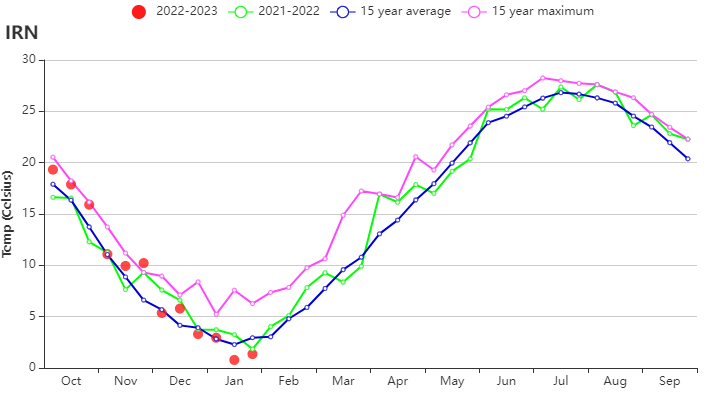
(d) Time series temperature profile (e) Maximum VCI
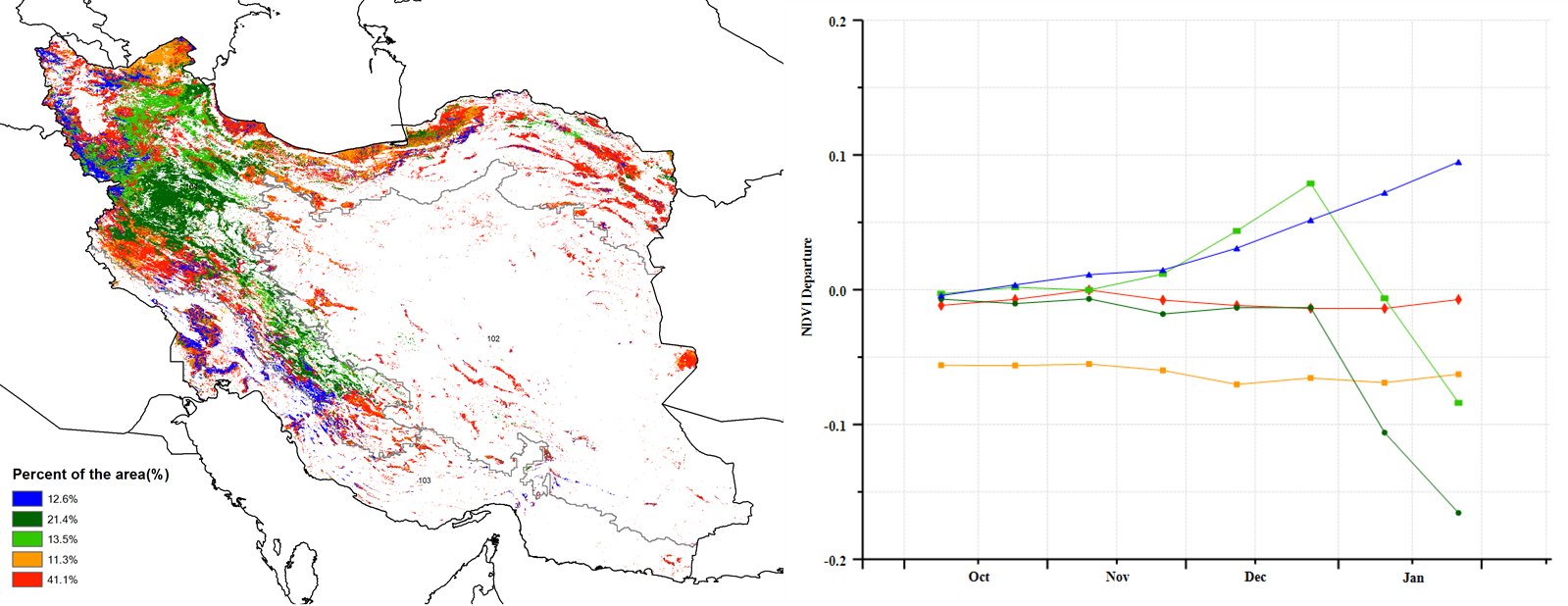
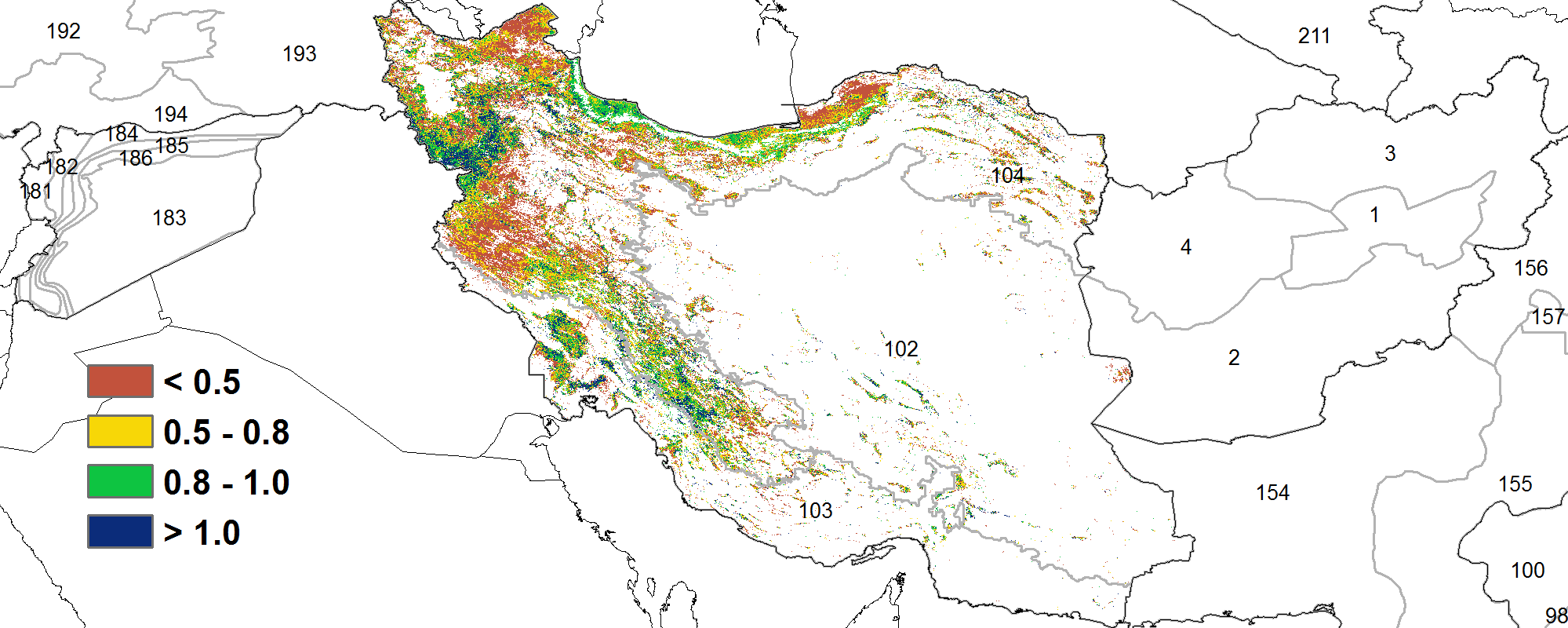
(f) Spatial NDVI patterns compared to 5YA (g) NDVI profiles
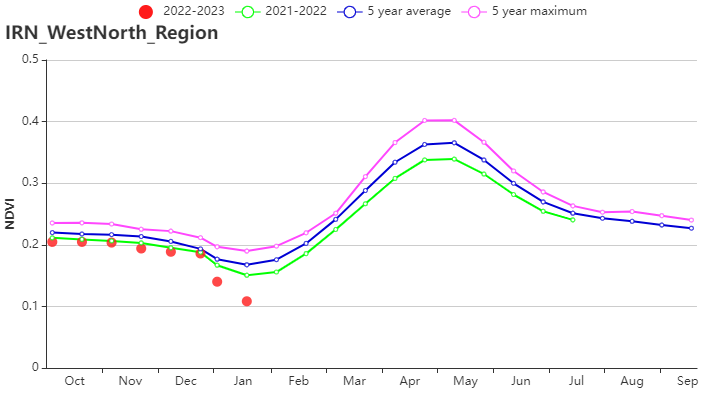
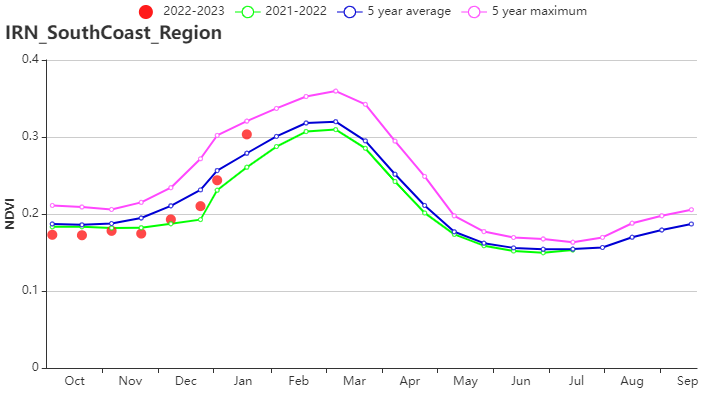
(h) Crop condition development graph based on NDVI (Semi-arid to sub-tropical hills of the west and north region (left) and Arid Red Sea coastal low hills and plains region (right))
Table 3.33. Iran's agroclimatic indicators by sub-national regions, current season's values and departure from 15YA, October 2022-January 2023
| Region | RAIN | TEMP | RADPAR | BIOMSS | ||||
| Current(mm) | Departure from 15YA(%) | Current(°C) | Departure from 15YA(°C) | Current(MJ/m2) | Departure from 15YA(%) | Current(gDM/m2) | Departure from 15YA(%) | |
| Arid Red Sea coastal low hills and plains | 169 | 12 | 19.4 | 1.5 | 831 | -3 | 507 | 12 |
| Semi-arid to sub-tropical western and northern hills | 159 | -21 | 7.0 | 0.6 | 740 | 1 | 336 | -13 |
Table 3.34. Iran's agronomic indicators by sub-national regions, current season's value and departure from 5YA, October 2022-January 2023
| Region | CALF | Maximum VCI | |
| Current(%) | Departure from 5YA(%) | Current | |
| Arid Red Sea coastal low hills and plains | 25 | 22 | 0.64 |
| Semi-arid to sub-tropical western and northern hills | 9 | -11 | 0.54 |
