This reporting period covers the harvesting period in this major production zone (MPZ). In the coastal regions, the harvest of the second season tuber crop, cassava, started in January. In the rest of the region, harvesting of rice, millet and sorghum crops was underway and concluded in January 2023. The MPZ relies significantly on imports of cereals, mostly of wheat and rice, to cover its domestic requirements. For Nigeria, cereal imports are forecasted at a near‑average level of 8.1 million tonnes.
With respect to the climatic indicators for the region, the estimated average rainfall was 163 mm (-22%). At the country level, rainfall deficits were observed for Liberia (416 mm -13%), Sierra Leone (380 mm -7%), Equatorial Guinea (1,434 mm +9%), Togo (57 mm -40%), Burkina Faso (6 mm -77%), Nigeria (125 mm -33%), Ghana (125 mm -35%), Côte d'Ivoire (195 mm -24%) and Guinea (210 mm +6%). Based on the Vegetative Health Index (VHI), localized areas of severe to moderate drought stress were observed, mainly in Nigeria. The average temperature of the MPZ varied from 22.8°C (Equatorial Guinea) to 25.9°C (Guinea Bissau) with an estimated regional average of 24.5°C (-0.6°C) and solar radiation was 1,220 MJ/m2 (-1%) while the regional accumulated biomass production potential decreased by 9%. The cultivated arable cropped area (CALF) for the region was 95% (-0.2%), with Nigeria at 89% (+4%). As an indication of good crop conditions, the regional maximum vegetation condition index (VCIx) attained a favourable value of 0.89. These CropWatch indicators showed stable, but slightly drier-than-usual climatic conditions. In general, conditions were close to normal.
Figure 2.1 West Africa MPZ: Agroclimatic and agronomic indicators, October 2022- Januray 2023.
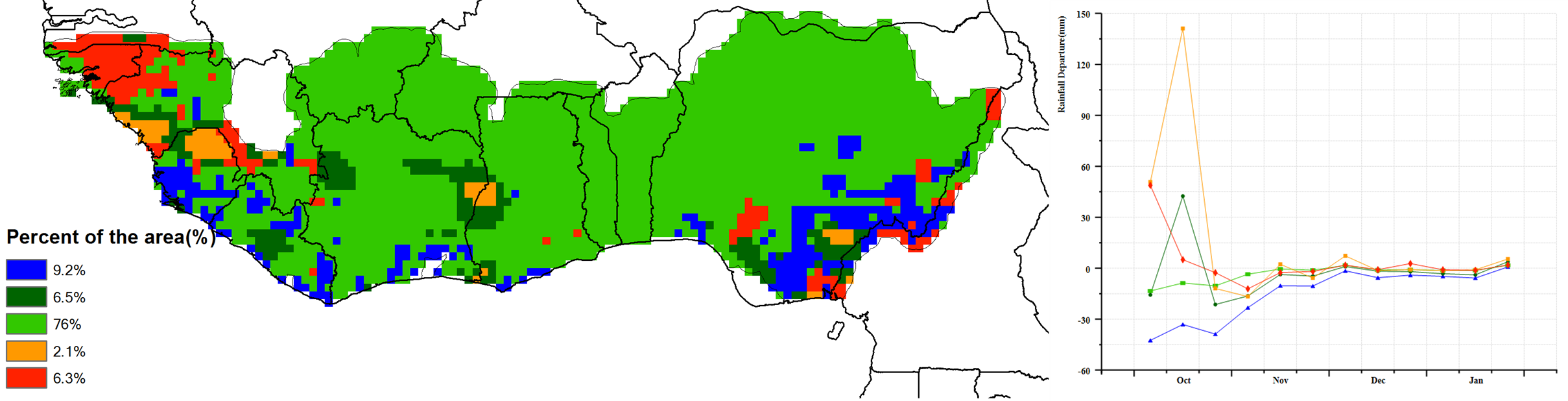
a. Spatial distribution of rainfall profiles b. Profiles of rainfall departure from average (mm)
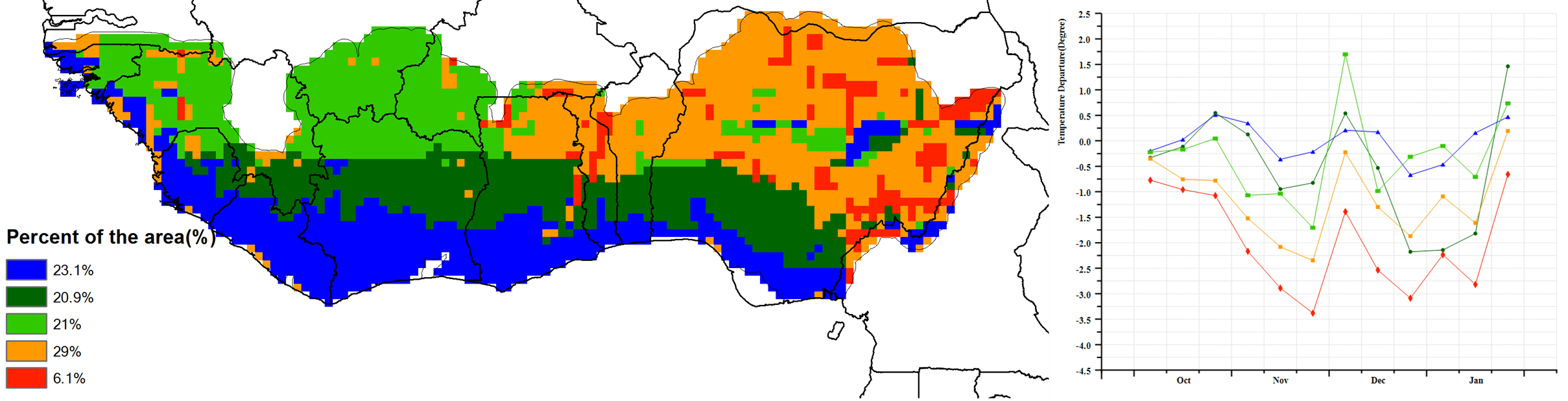
c. Spatial distribution of temperature profiles d. Profiles of temperature departure from average (mm)
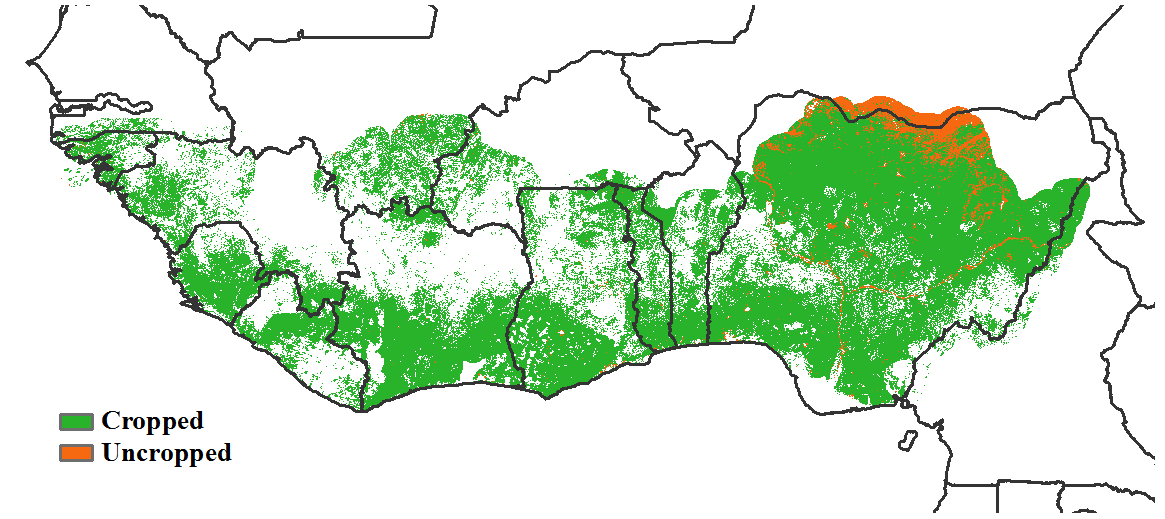
e. Cropped and uncropped arable land
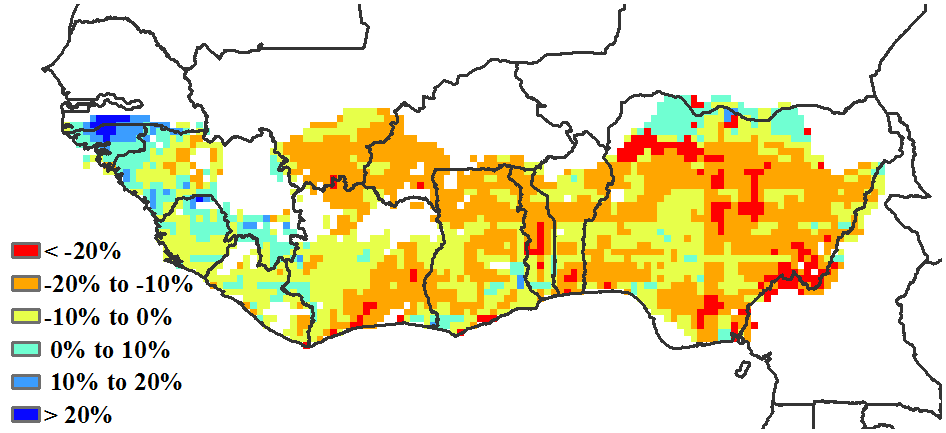
f. Potential biomass departure from 5YA
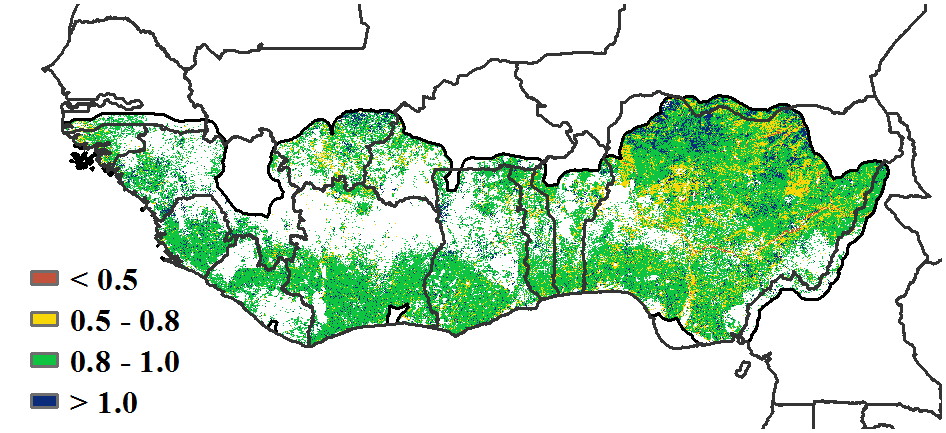
g. Maximum VCI
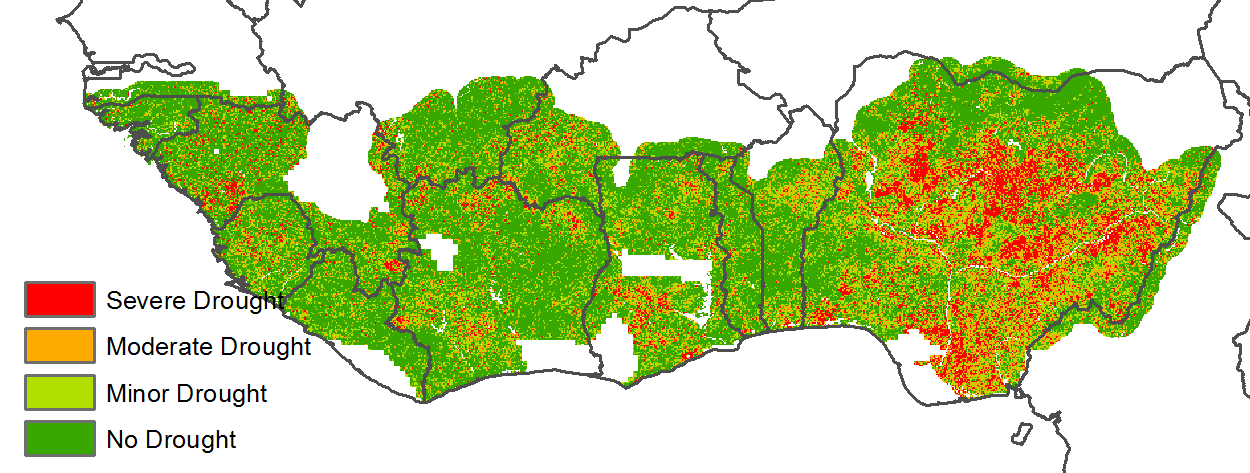
h. VHI Minimum
