本监测期涵盖了华南区晚稻从播种到收获的完整周期。基于NDVI的作物生长过程线显示,在监测期大部分时间内,作物长势接近但略低于平均水平。
Late rice completed its complete cycle from sowing to harvesting in southern China during the monitoring period. The condition of the crop was generally close to but below average, according to the NDVI development curves.
监测期内,华南区累计降水量达到1172mm,相比平均水平偏低2%,其中广西自治区降水偏高5%,广东省偏高4%,两省降水量均超过了1100mm,云南省偏高 3%,福建省则偏低了5%,云南省和福建省的降水量也超过了900mm。
Regionally, rainfall reached 1172 mm, which was 2% lower than the average; provincial departures were the following: +4% in Guangdong, +3% in Yunnan, -5% in Fujian, and +5% in Guangxi. In Guangdong and Guangxi RAIN exceeded 1100 mm, while in Yunnan and Fujian it exceeded 900 mm.
华南地区监测期间的平均气温约为22.3°C,相比平均水平偏高0.2°C,潜在生物量偏高2%。其中,福建省,广东省和云南省的潜在生物量水平分别偏高了8%,1%和8%,而广西自治区的生物量水平却呈下降趋势,下降了3%。在省级尺度,潜在生物量的距平与光合有效辐射距平相对一致,表明光照在供水充足时,是作物生长的主要限制因素。监测期间华南地区的最佳植被状况指数达到了0.90,主产区几乎全部区域最佳植被状况指数均高于0.80。
The average temperature during the monitoring period in South China was 22.3°C, which was above average by 0.2°C.BIOMSS is 2% higher than average. The biomass index of Fujian, Guangdong and Yunnan increased by 8%, 1% and 8%, respectively, while Guangxi recorded a 3% drop. At the provincial level, biomass changes are consistent with sunlight (RADPAR), which is the dominant limiting factor for crop growth when water supply is sufficient. The average VCIx of the South China region during the monitoring period was 0.90, and almost all regions presented above 0.80 VCIx during this monitoring period.
NDVI距平聚类分析结果显示,华南区约17.2%的耕地上作物长势在监测期内始终低于平均水平,而其他大部分地区作物长势总体处于或接近平均水平。总体而言,华南地区作物长势略低于平均水平。
NDVI departure clustering analysis revealed the continous below average condition crops were mostly located in south-western Guangdong Province, covering 17.2% of the total cropland area. Overall, the crops in Southern China was slightly below average.
Figure 4.13. Crop condition Southern China region, July-October 2019
图4.13 2019年7月-10月华南地区作物生长状况
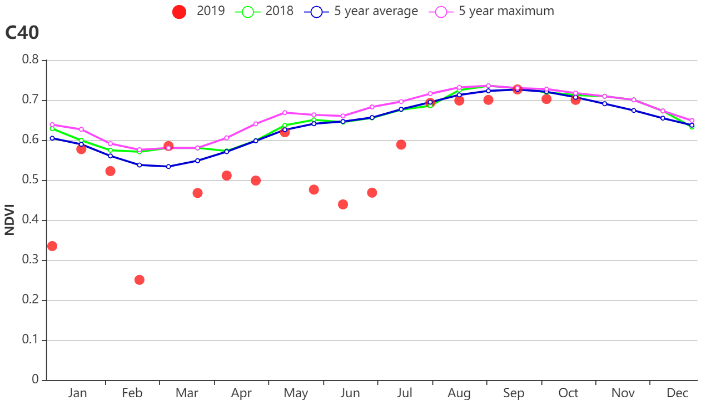
(a) 基于 NDVI 的作物生长过程线

(b) 降水过程线
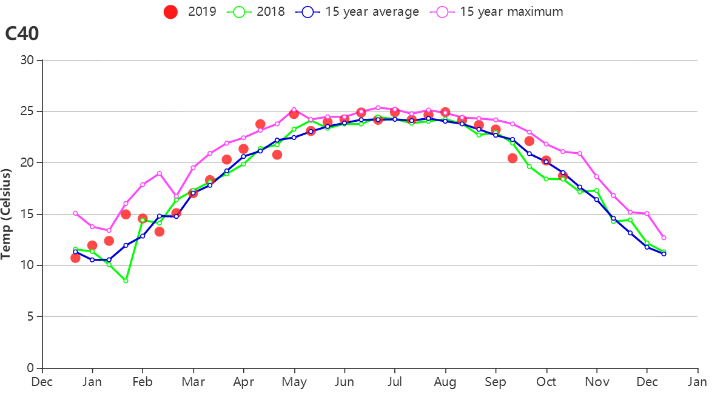
(c)温度过程线
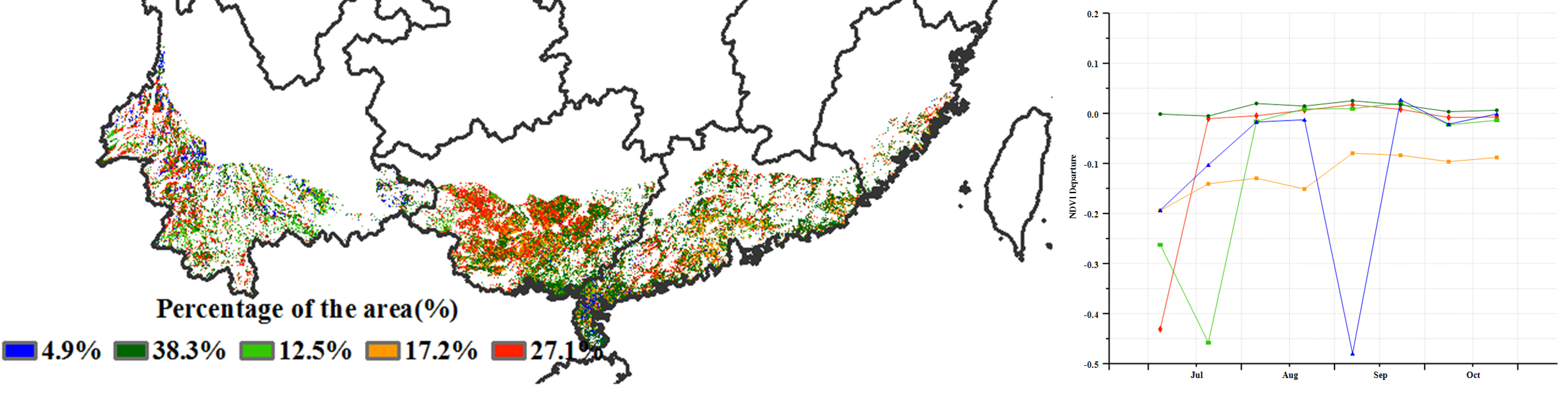
(d) NDVI 距平聚类图(与 5 年平均相比) (e)NDVI 距平聚类类别曲线

(f) 最佳植被状况指数

(g) 潜在生物量
