The monitoring period covers the whole cycle of summer maize from July to late September, as well as the sowing and early growing season of winter wheat from early October. The NDVI development graph displays generally slightly below-average crop condition.
本监测期覆盖了夏玉米的完整生育期以及冬小麦的播种期和生长早期。基于NDVI的作物生长过程线显示,该地区的作物长势总体上略低于平均水平。
The NDVI values were below 5YA from July to early August, but then improved to 5YA until harvesting. For early October, coinciding with early winter wheat, NDVI values fell slightly to below 5YA again.
秋粮作物播种至8月初,主产区NDVI值始终低于近5年平均水平,主要原因是前期的旱情阻碍了秋粮作物的早期生长发育。8月初台风“利奇马”带来的充沛降水促进了作物生长,作物长势恢复至平均水平,并维持该状况直到秋粮作物收获。之后冬小麦陆续播种,在小麦生长早期,NDVI值略低于近5年平均水平。
Agro-climatic conditions include a 26% decline in precipitation compared to average, affecting mainly early growth of maize. The temperature and the radiation rose by 0.8℃ and 4% compared to 15YA, respectively. The slight drop in NDVI during the growing season of maize may be influenced mainly by poor precipitation, which led directly to a 1% drop in BIOMSS. Besides, low NDVI values in early October had no effect on the BIOMSS index. The maximum VCI value for Huanghuaihai was 0.89.
农气状况监测结果显示,全区累计降水较平均水平偏低26%,造成玉米生长初期发育相对迟缓;平均气温和光合有效辐射分别较平均水平偏高0.8℃和4%,光温水三要素综合作用使得潜在生物量较平均水平偏低1%。此外,10月初由于夏粮作物刚仍处于生长早期,偏低的NDVI不会对后期作物生长产生显著影响。监测期内黄淮海区的最佳植被状况指数为0.89。
As shown by NDVI clusters and profiles, 20.7% of cropland over northern Anhui and Jiangsu, as well as some scattered areas across the whole region, displays average condition during almost the whole period. 41.9% of cropland over southern Hebei, western Shandong and northern Henan suffered below-average condition before August and recovered to average during September. Remaining areas had negative NDVI departure values all the time. The spatial distribution of biomass departures displays a drop not exceeding 10%; more significant reductions are noted in Beijing and some scattered areas in Shandong and Henan. Increases only occur in eastern Henan and northern Anhui and Jiangsu.
NDVI距平聚类分布图及其过程线显示,位于安徽北部和江苏北部的耕地区域以及其余一些零散地区的作物长势在整个监测期内始终处于平均水平。这些耕地的面积约占该区域总耕地面积的20.7%。河北南部、山东西部和河南北部,约41.9%的耕地区域在8月之前低于平均水平,8月初的充沛降水促使作物在9月份恢复到平均水平。其余地区的耕地在监测期内的作物长势始终低于平均水平。潜在生物量距平分布图显示,大部分地区的潜在生物量较平均水平均略偏低(偏低幅度不超过10%),但北京和山东、河南等地的一些零星地区偏低幅度较为明显。潜在生物量的偏高仅出现在河南东部、安徽北部和江苏北部等地。
In general, crop condition in Huanghuaihai was below average due to severe water stress at early growing stage, but recovered to average level since mid-August.
总体而言,黄淮海区的作物生长早期的水分亏缺对作物生长产生一定影响,导致作物长势略低于平均水平,但在8月中旬后逐渐恢复至平均水平。
图4.14 2019年7月-10月黄淮海区作物长势
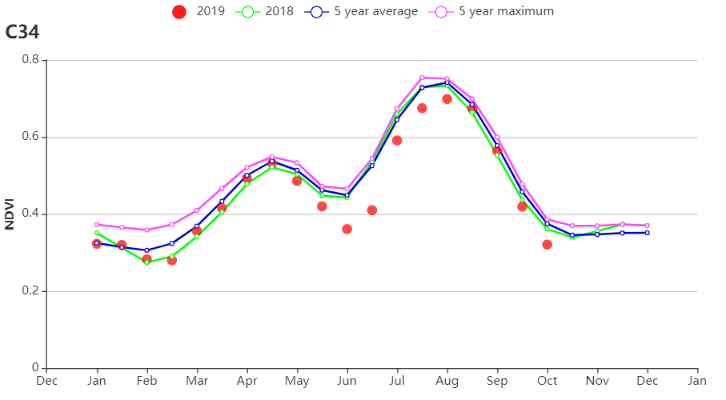
(a) 基于NDVI的作物生长过程线

(b) 降水过程线
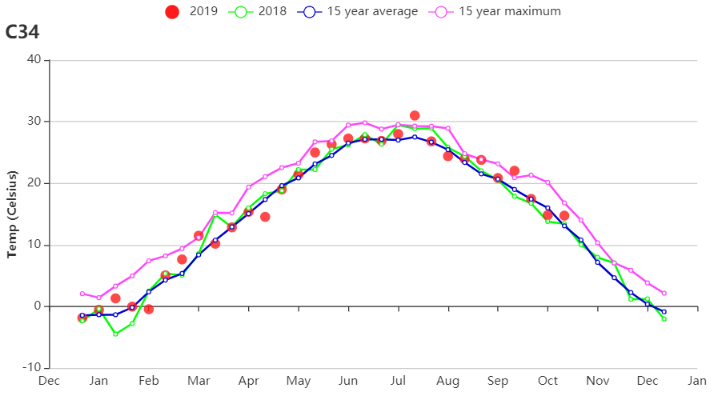
(c) 气温过程线
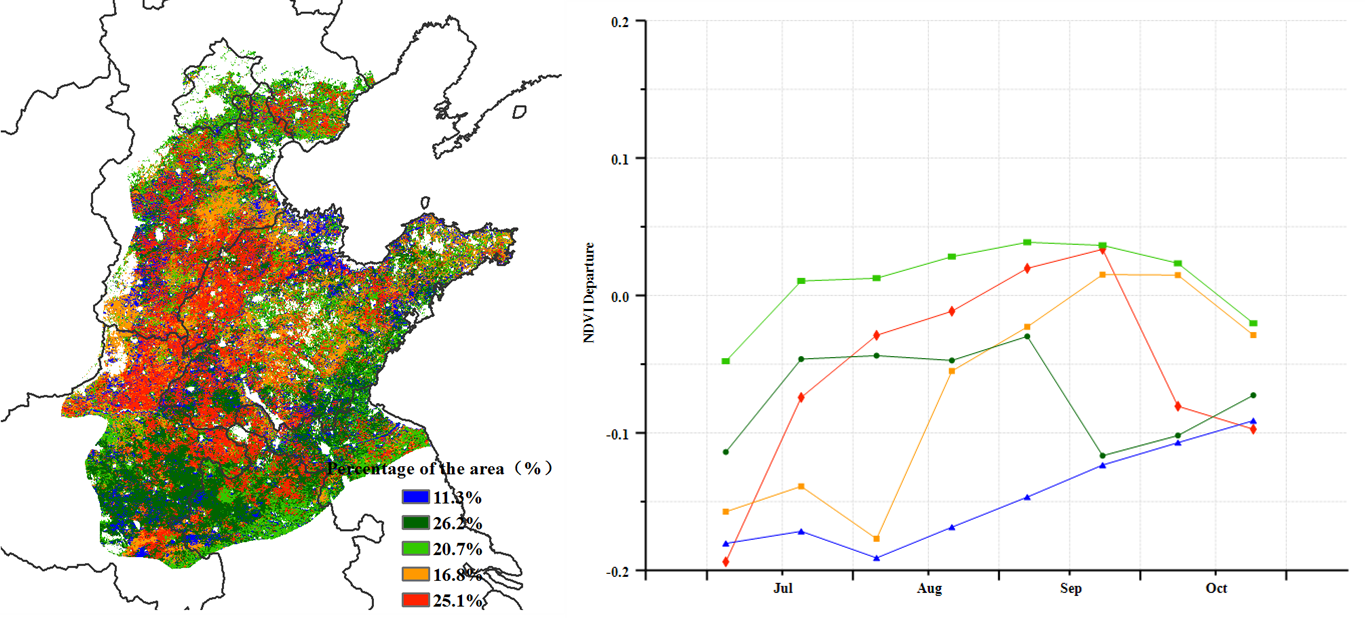
(d) NDVI距平聚类分布图(与5年平均相比) (e) NDVI距平聚类类别曲线
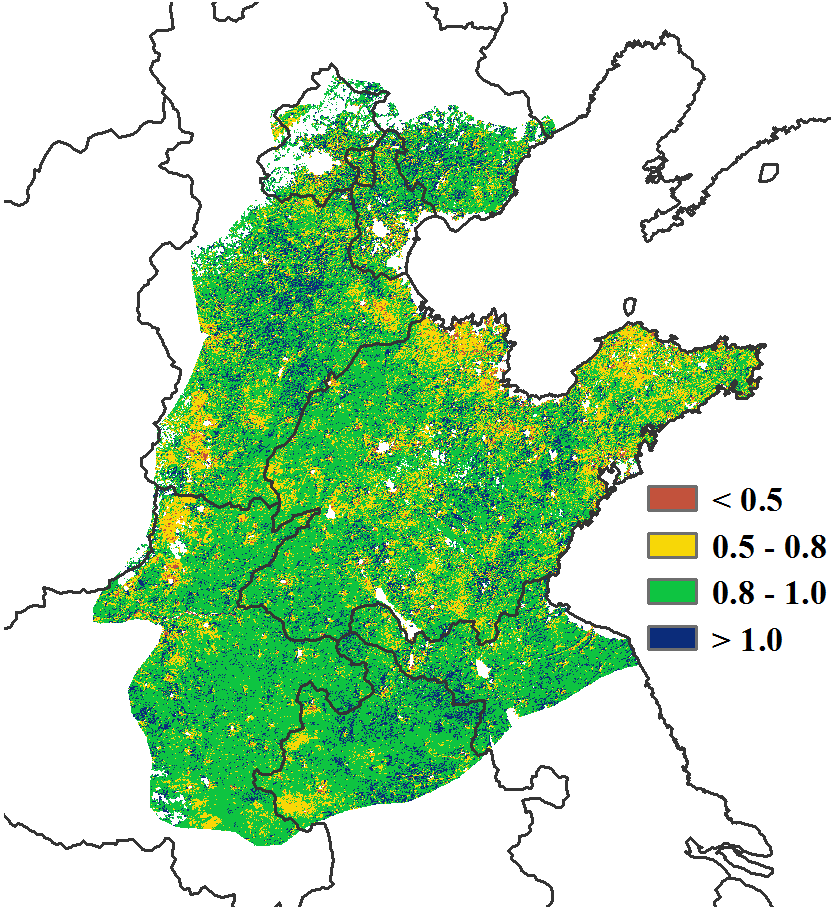
(f) 最佳植被状况指数

(g) 潜在生物量距平
