This current monitoring period covers the sowing and the first half of the growing season of main crops in the Northeast of China (April to July 2023). CropWatch Agroclimatic Indicators (CWAIs) show that precipitation was slightly above average. The total precipitation increased by 1%. It was below the average level in May and June, and above the average level in July. The photosynthetically active radiation was close to average, and the temperature was below average (TEMP 0.2℃). This resulted in a potential biomass estimate that was 2% below the fifteen-year average level. Most parts of Heilongjiang province and the western part of Jinlin province were below average due to low precipitation, causing a mild drought.
本监测期覆盖了东北地区主要作物的播种期,且作物至7月末逐渐达到生长高峰期。CropWatch农气指标显示,该区域降水量略高于平均水平(+1%),5月和6月低于平均水平,7月高于平均水平。光合有效辐射接近平均水平,气温低于平均水平(0.2℃)。农气条件综合作用使得东北区潜在生物量与过去15年平均水平相比偏低2%。黑龙江省西部和吉林省西部大部分地区由于降水量较低造成轻度干旱,导致潜在生物量低于平均水平。
The crop conditions during the monitoring period were slightly below average before July and recovered to average levels till the end of July. Meanwhile, great spatial variations existed in the region. As shown by NDVI clusters and profiles, 27.4% of cropland experienced a steady decline until mid June and then increased to average levels. This area was mostly distributed in Heilongjiang province and western Jilin province. About 18.6% of cropland in the region was mostly below average. It was mainly located in western Heilongjiang province, indicating that crops in this area were in relatively poor condition. About 26% of cropland was slightly negative, mainly concentrated over Liaoning province. Most parts of the Northeast of China were below average from April to June and improved in July, and this is due to a slight drought caused by below average precipitation in the early stage. In addition, the maximum VCI shows that all provinces of the Northeast of China were above 0.8, except for a small part of western Heilongjiang province due to drought and western Jilin province due to local drought and floods in the early stage. On the other hand, flooding that occurred in early August negatively affected crops locally in Wuchang, Shangzhi and Mudanjiang in central southern Heilongjiang province and Shulan in eastern Jilin province, accounting for about 4% of the cropland area in the region. All in all, crop development until June was below average but recovered to average levels in July. Prospects for crop production are average.
7月前监测期间的作物状况略低于平均水平,直到7月底才恢复到平均水平。同时,该地区存在较大的空间差异。从NDVI距平聚类分析结果来看,全区27.4%的耕地作物长势在6月中旬之前逐渐恶化,之后随着水分条件的改善,长势恢复到平均水平,主要分布在黑龙江省和吉林省西部;约18.6%的耕地作物长势在监测期内始终低于平均水平,主要位于黑龙江省西部,表明该地区的作物状况相对较差;约26%的耕地作物长势略低于平均水平,集中分布在辽宁;东北大部分地区4-6月的作物长势低于平均水平,主要原因是前期降水低于平均水平导致的轻度干旱,多数地区的作物长势在7月份均有所改善。此外,最佳植被状况指数空间分布图显示,除黑龙江省西部少部分地区和吉林省西部受前期干旱影响外,东北大部VCIx均在0.8以上。同时,8月初发生的洪水对黑龙江省中南部的五常、尚志和牡丹江以及吉林省东部的舒兰等地作物产生了负面影响,洪灾影响面积约占东北区耕地面积的4%。总的来说,东北地区作物生产形势处于常年平均水平。
图4.8 2023年4月-7月东北区作物长势
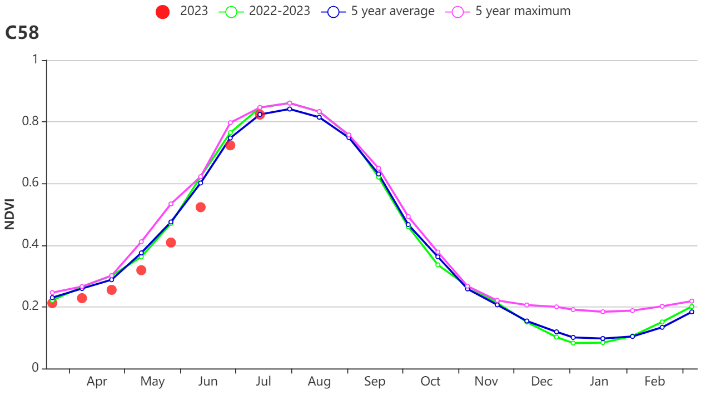
(a) 基于NDVI的作物生长过程线
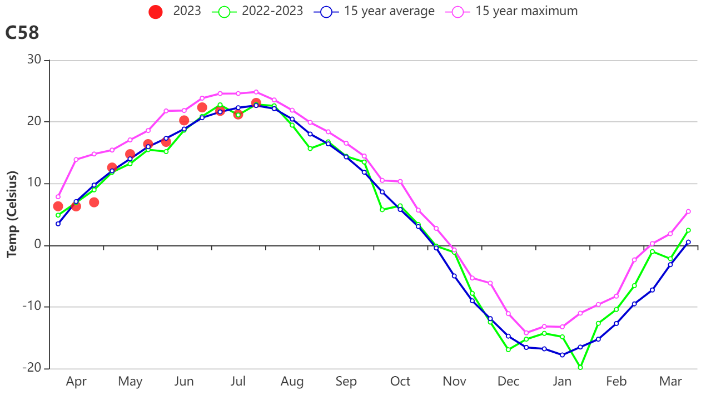
(b) 时间序列(旬)温度过程线
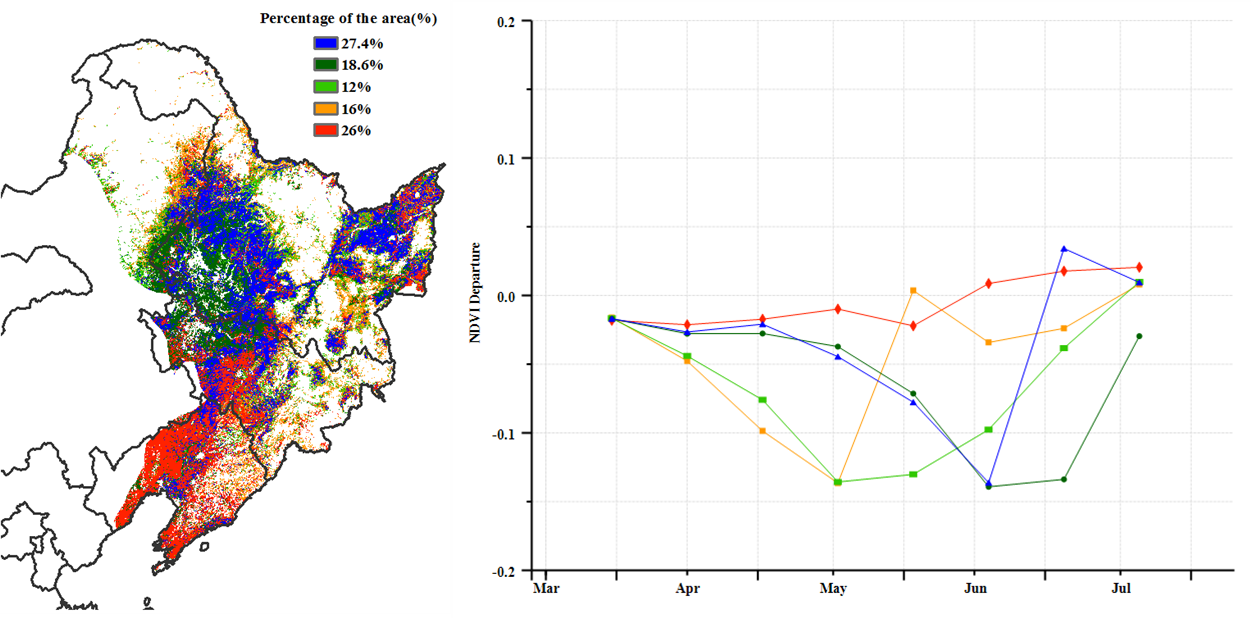
(c)NDVI距平聚类图
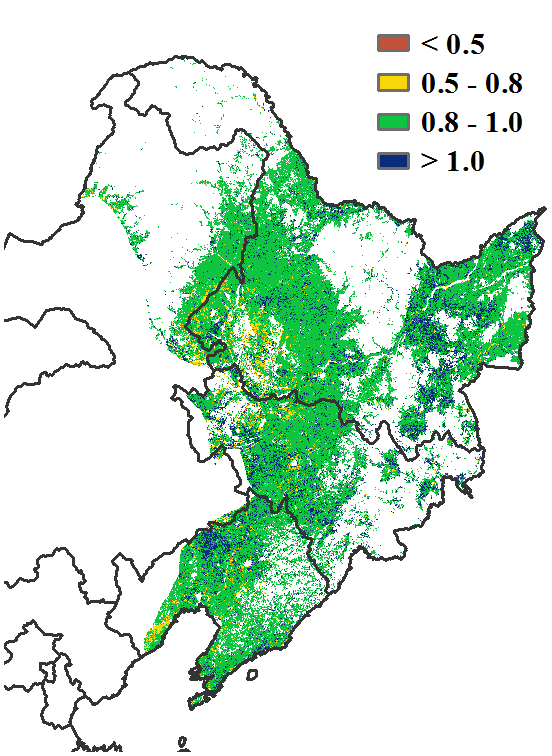
(d)最佳植被状况指数
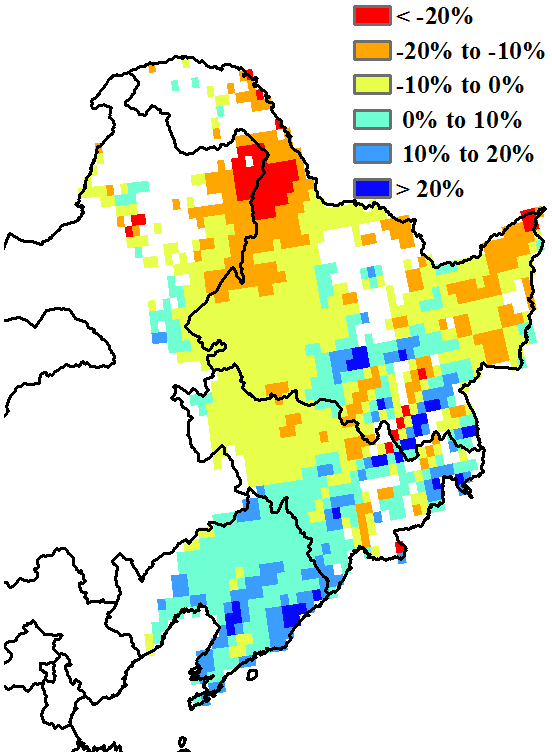
(e) 潜在生物量距平(与15年平均相比)
