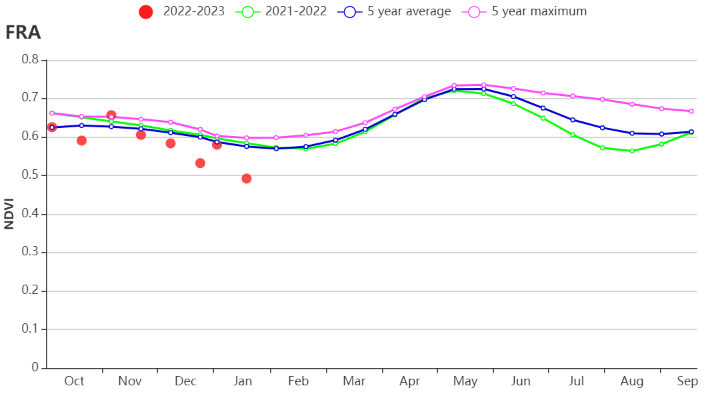
This monitoring period covers the harvest of maize as well as sowing and the early growth period of winter wheat. CropWatch agro-climatic indicators show that the temperatures were above the average over most of the monitoring period (TEMP +1.5°C), but lower than average in early December and late January. There was a cold spell in January, when the average temperature hovered around 1°C. Snow fell in many places of France. RAIN was 8% below average, while sunshine (RADPAR) was 4% above. Due to favorable temperature and sunshine conditions, the biomass production potential (BIOMSS) is estimated to have increased by 8% nationwide compared to the 15-year average. The national-scale NDVI development graph shows that the NDVI values were overall below the 5 year average. Only in early November they were above average. The sharp drops in NDVI were most likely due to cloud cover, fog or snow on the ground. The cropped arable land fraction (CALF) departure value was above average by 1%. The spatial distribution of maximum VCI (VCIx) across the country also reached a range of 0.82-0.96. Overall, the precipitation deficit caused slightly unfavorable growth conditions for some France’s agricultural regions.
本监测期涵盖了法国玉米的收获期以及冬小麦的播种和生长早期。CropWatch农气指标监测结果表明,与过去15年平均水平相比,平均气温整体偏高1.5°C,但于12月初及1月底低于平均值。1月份出现寒潮,平均气温为1°C左右,法国多地均有降雪。本监测期内降水量整体偏低8%,同时光合有效辐射偏高4%。受有利的气温和光照条件影响,法国全国尺度潜在累积生物量与过去15年平均水平相比偏高8%。基于NDVI作物生长过程线显示,法国作物长势整体低于近5年平均水平,仅在11月初高于平均水平。NDVI 值的急剧下降很可能是由于地面上的云层、雾或雪造成的。耕地种植比例略偏高1%。法国整体的最佳植被状况指数达到0.82-0.96之间。总的来说,降水量不足导致了法国部分农业地区作物长势不佳。
Regional analysis
Considering cropping systems, climatic zones and topographic conditions, additional sub-national details are provided for eight agro-ecological zones. They are identified on the maps by the following numbers: (78) Northern barley region, (82) Mixed maize/barley and rapeseed zone from the Center to the Atlantic Ocean, (79) Maize-barley and livestock zone along the English Channel, (80) Rapeseed zone of eastern France, (75) Massif Central dry zone, (81) Southwestern maize zone, (76) Eastern Alpes region and (77) the Mediterranean zone.
区域分析
基于种植系统、气候分区以及地形条件,可将法国细分为8个农业生态区,分别是(78)北部大麦区;(82)西部玉米、大麦和油菜混种区;(79)西北玉米和大麦混种区;(80)油菜种植区;(75)中部干旱区;(81)西南玉米区;(76)东部高原区,以及(77)地中海气候区。
In the Northern barley region, warmer weather was observed (TEMP +1.1°C) while RADPAR was above average (+10%) but RAIN was below average (-6%). The potential BIOMSS increased by 6% when compared to the 15-year average. The CALF was higher than the average (+1%), and VCIx was 0.89. Crop condition development based on NDVI for this region was below the 5-year average for most of the monitoring period, especially in December, but higher than average in early November and January.
监测期内,与过去15年平均水平相比,北部大麦区平均气温略偏高1.1°C,同时光合有效辐射偏高10%,而降水量偏低6%。该区域潜在累积生物量较过去15年平均水平偏高6%。耕地种植比例较平均值偏高1%,最佳植被状况指数为0.89。基于NDVI作物生长过程线显示,监测期内该区域作物长势低于近5年平均水平,特别是在12月,但在11月初及1月时高于平均水平。
In the Mixed maize/barley and rapeseed zone from the Center to the Atlantic Ocean, warmer (TEMP +1.3°C) and drier (RAIN -9%) conditions were observed and RADPAR was above average by 3%. Potential BIOMSS was above average by 6% while the overall NDVI profile showed the regional crop conditions were higher than average levels, being below average in mid-October and mid-December only. The CALF was increased by 2%, and VCIx was relatively high, at 0.96.
CropWatch农气指标监测结果表明,西部玉米、大麦和油菜混种区的平均气温偏高1.3°C,光合有效辐射偏高3%,而降水量偏低9%。该区域潜在累积生物量偏高6%。NDVI作物生长过程线显示,该区域作物长势偏高于多年平均水平,仅在10月中旬及12月中旬低于平均水平。与过去15年平均水平相比,耕地种植比例较平均值偏高2%。最佳植被状况指数相对较高,为0.96。
In the Maize-barley and livestock zone along the English Channel, RADPAR and TEMP were above average by 6% and 0.8°C. RAIN was also higher than the average (+7%). Potential BIOMSS increased by 8%. CALF was average and VCIx was recorded at 0.87. The NDVI profile trended close to the average, except for mid-October and late December, when RADPAR was below average.
在西北玉米和大麦混种区,与过去15年平均水平相比,光合有效辐射与气温分别偏高6%与0.8°C,而降水量则偏低7%,潜在累积生物量偏高8%。该区域耕地种植比例与平均水平持平,而最佳植被状况指数整体达到0.87。总体来说除10月中旬及12月受光合有效辐射低的影响外,该区域作物生长状况接近平均水平。
In the Rapeseed zone of eastern France, RAIN in this monitoring period was 5% lower than the 15-year average, while TEMP increased by 1.5°C and RADPAR was increased by 5%. BIOMSS was about 12% higher than average with a high VCIx level (0.96). CALF was above average by 1%. The NDVI profile showed great fluctuation during the monitoring period. It was above average in October and then below average in November to January.
在油菜种植区,监测期内降水量较过去15年平均水平偏低5%,而气温偏高1.5°C,光合有效辐射则偏高5%。潜在累积生物量偏高12%,同时最佳植被状况指数为0.96。耕地种植比例较平均值偏高1%。NDVI作物生长过程线在本监测期内出现很大波动,显示作物生长状况于10月高于平均水平,但在11月至1月低于平均水平。
In the Massif Central dry zone, TEMP and RADPAR were 1.4°C and 3% higher than the average, respectively, while RAIN decreased by 12%. The VCIx was 0.96 and potential BIOMSS increased by 10%. CALF was average. Crop conditions based on the NDVI profile indicated that growth conditions were above average before November and below average after November, especially in January when the cold spell hit France.
在中部干旱区,监测期内气温和光合有效辐射分别比过去15年平均水平偏高1.4°C 和3%,而降水量偏低12%。最佳植被状况指数为0.96,而潜在累积生物量偏高10%。耕地种植比例处于平均水平。NDVI作物生长过程线显示,11月前作物生长状况高于平均水平,而11月后作物生长状况则低于平均水平,特别是在1月有寒潮到来时。
The Southwestern maize zone is one of the major irrigated regions in France. The regional NDVI profile presented a below average trend, but it was close to the average in mid-November and early December. The VCIx recorded moderate levels (0.90) and potential BIOMSS was 7% higher than average. RAIN in the period was 8% lower than average. TEMP was 1.2°C higher, while RADPAR increased by 1%. CALF was above average by 1%.
西南玉米区是法国的主要灌溉地区之一。该区域的NDVI作物生长过程线显示监测期内除11月中及12月初作物生长状况接近平均水平外,作物生长状况总体低于多年平均水平,同时最佳植被指数处于中等水平(0.90),而潜在累积生物量较平均水平偏高7%。在监测期内,该地区的降水量较多年平均偏低8%,温度偏高1.2°C,同时光合有效辐射偏高1%,耕地种植比例偏高1%。
In the Eastern Alpes region, crop conditions presented a slightly above average trend except in January. RADPAR and TEMP in the region were 4% and 1.7°C higher than average, while RAIN was 7% below the average. Potential BIOMSS was also higher than the 15-year average (+14%). VCIx for the region was recorded at 0.94. CALF increased by 1%.
在东部高原区,作物长势表现出了除1月外略高于多年平均水平的趋势。监测期内,该地区的光合有效辐射和温度较多年平均分别偏高4%和1.7°C, 而降水量偏低7%。该区的潜在累积生物量较过去15年平均水平偏高14%,最佳植被指数为0.94,耕地种植比例偏高1%。
In the Mediterranean zone, NDVI recorded a below-average trend. The region recorded a relatively low VCIx level (0.82). RADPAR and TEMP were above the average (2% and +2.7°C, respectively), while RAIN was significantly lower than average by 24%. CALF also increased by 1%. Potential BIOMSS was above average by 5%.
地中海气候区的NDVI作物生长过程线显示,作物长势低于多年平均水平。该地区最佳植被状况指数为0.82,光合有效辐射和气温均高于15年平均水平,分别偏高2%、2.7°C,同时降水量严重偏低24%。耕地种植比例同样偏高1%,潜在累积生物量与过去15年平均水平相比偏高5%。
图3.5 2022年10月-2023年1月法国作物长势
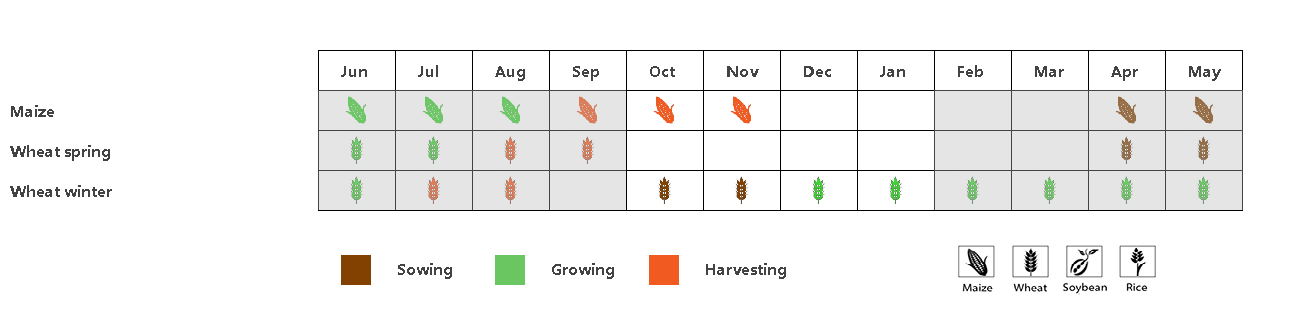
(a). 主要作物物候历
![]()
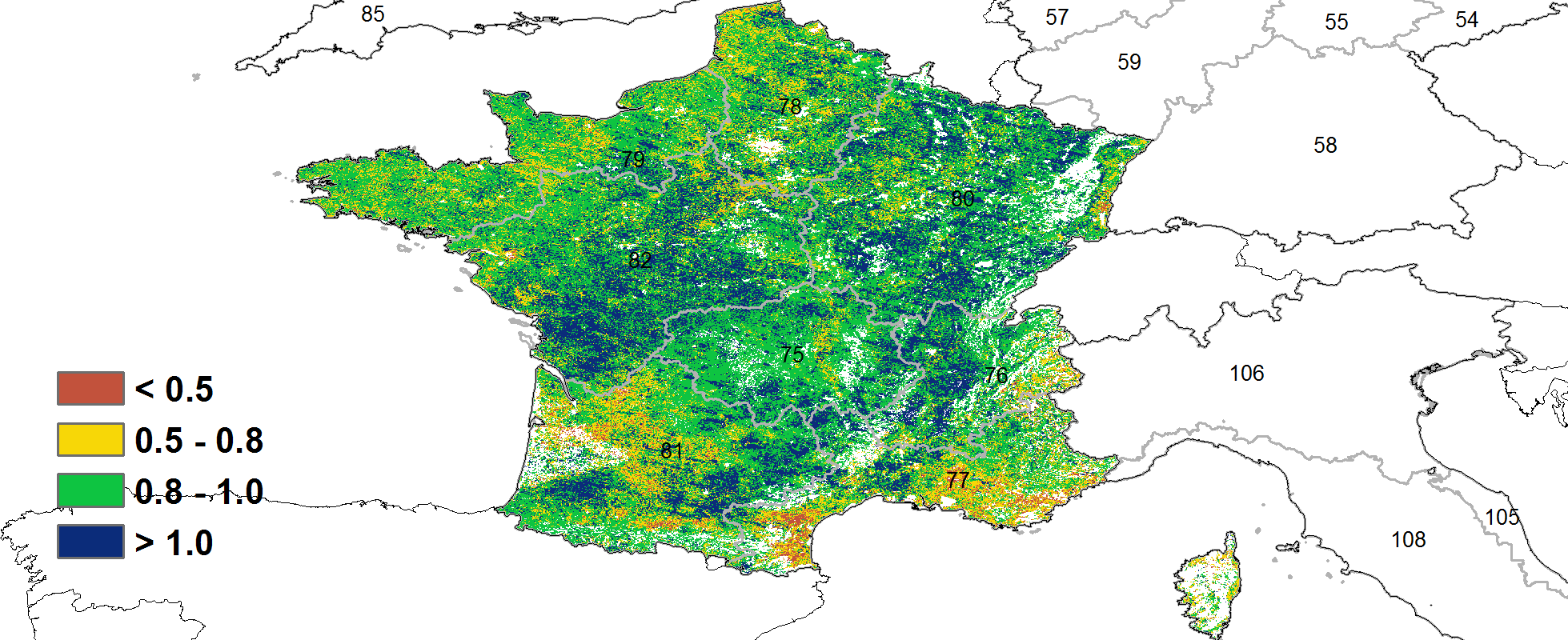
(b) 基于NDVI的作物生长过程线 (c) 最佳植被状况指数
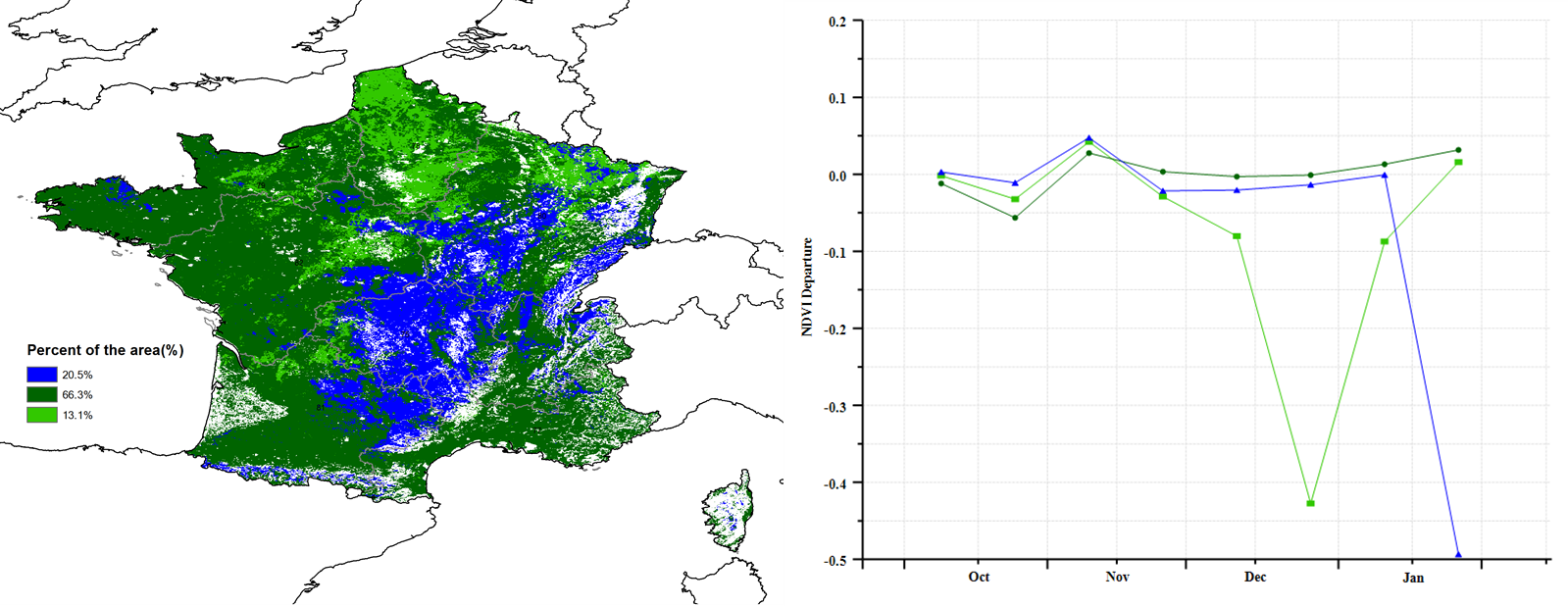
(d)NDVI距平空间聚类图(与5年平均相比) (e) NDVI距平聚类过程线

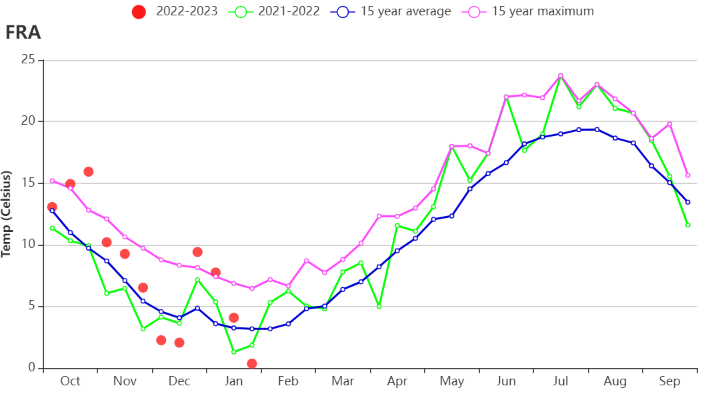
(f) 降水时间序列过程线 (g)温度时间序列过程线
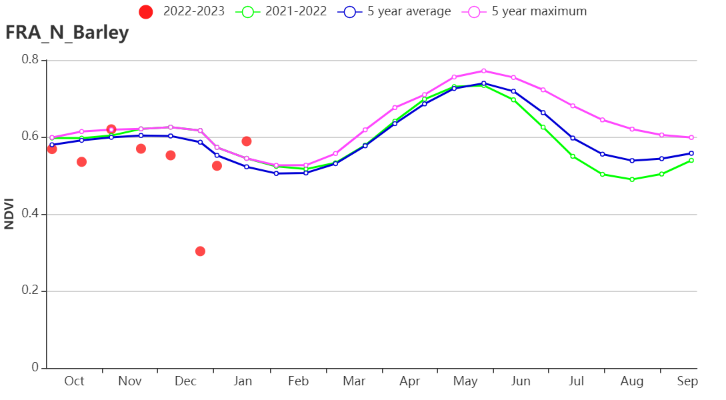
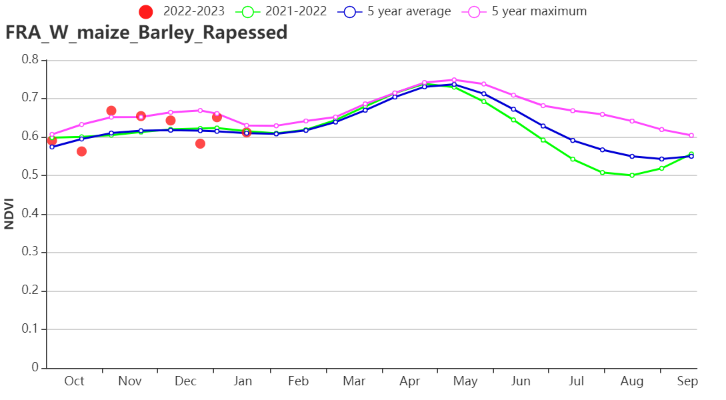
(h)基于 NDVI 的作物生长过程线(北部大麦区(左)和西部玉米区、大麦和油菜籽区
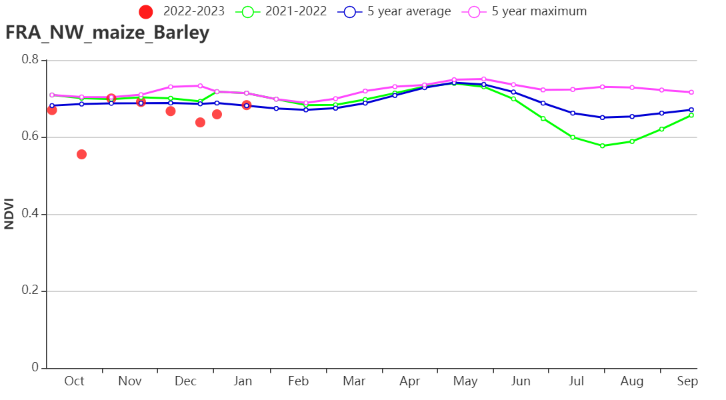
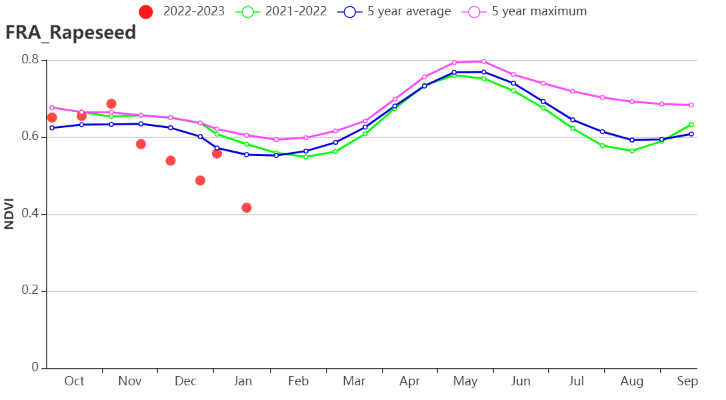
(i)基于 NDVI 的作物生长过程线(西北玉米和大麦区(左)和油菜种植区(右))
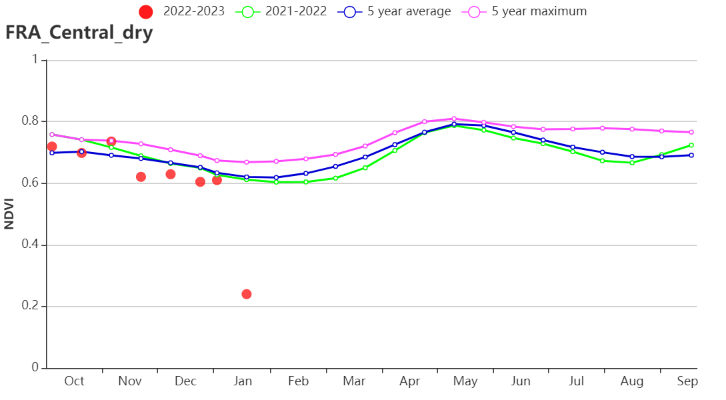
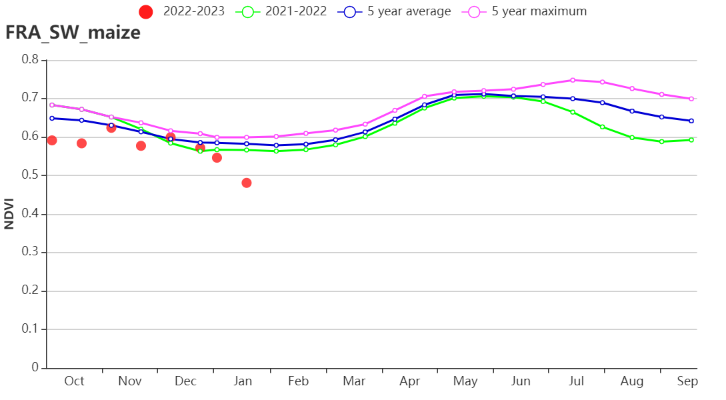
(j) 基于 NDVI 的作物生长过程线(中部干旱区(左)和西南玉米区(右))
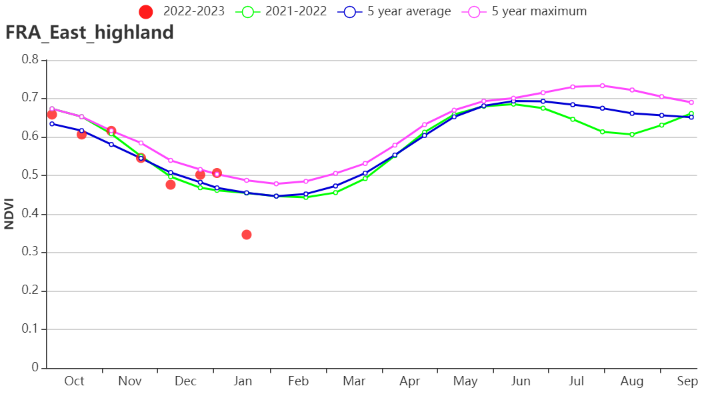
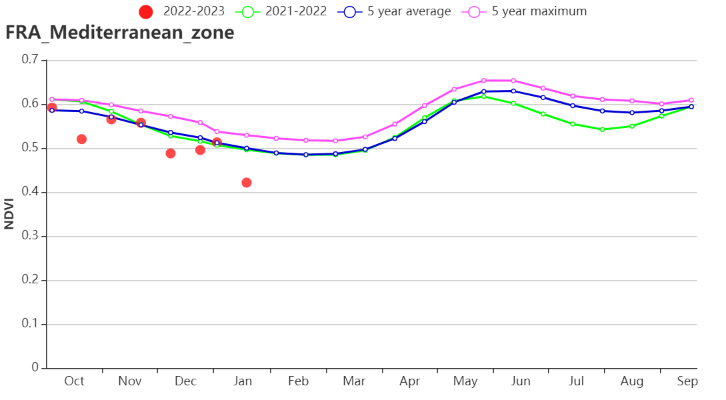
(k) 基于 NDVI 的作物生长过程线(东部高原区(左)和地中海气候区(右))
表3.2 法国农业生态分区2022年10月-2023年1月与过去15年(15YA)同期农业气象指标
区域 | 累计降水 | 平均气温 | 光合有效辐射 | 潜在生物量 | ||||
当前值(mm) | 距平(%) | 当前值(℃) | 距平(℃) | 当前值(MJ/m2) | 距平(%) | 当前值(gDM/m2) | 距平(%) | |
北部大麦区 | 332 | -6 | 7.8 | 1.1 | 265 | 10 | 628 | 6 |
西部玉米、大麦和油菜混种区 | 331 | -9 | 9.3 | 1.3 | 320 | 3 | 670 | 6 |
西北玉米和大麦混种区 | 431 | 7 | 9.0 | 0.8 | 281 | 6 | 702 | 8 |
油菜种植区 | 394 | -5 | 6.7 | 1.5 | 298 | 5 | 602 | 12 |
中部干旱区 | 351 | -12 | 6.9 | 1.4 | 357 | 3 | 605 | 10 |
西南玉米区 | 423 | -8 | 8.6 | 1.2 | 401 | 1 | 650 | 7 |
东部高原区 | 481 | -7 | 5.5 | 1.7 | 397 | 4 | 549 | 14 |
地中海气候区 | 322 | -24 | 9.0 | 2.7 | 462 | 2 | 569 | 5 |
表3.3 法国农业生态分区2022年10月-2023年1月与近5年(5YA)同期农情指标
区域 | 耕地种植比例 | 最佳植被状况指数 | |
当前值(%) | 距平(%) | 当前值 | |
北部大麦区 | 100 | 1 | 0.89 |
西部玉米、大麦和油菜混种区 | 100 | 2 | 0.96 |
西北玉米和大麦混种区 | 100 | 0 | 0.87 |
油菜种植区 | 100 | 1 | 0.96 |
中部干旱区 | 100 | 0 | 0.96 |
西南玉米区 | 99 | 1 | 0.90 |
东部高原区 | 95 | 1 | 0.94 |
地中海气候区 | 94 | 1 | 0.82 |
